Click here and press the right key for the next slide (or swipe left)
also ...
Press the left key to go backwards (or swipe right)
Press n to toggle whether notes are shown (or add '?notes' to the url before the #)
Press m or double tap to see a menu of slides

Systems, Models and Signature Limits
s.butterfill@warwick.ac.uk
first question
second question
outline
- two questions [done]
- a conjecture about systems
- predictions
- a conjecture about models
- predictions
first conjecture:
There are two (or more) systems for tracking others’ beliefs.
predictions:
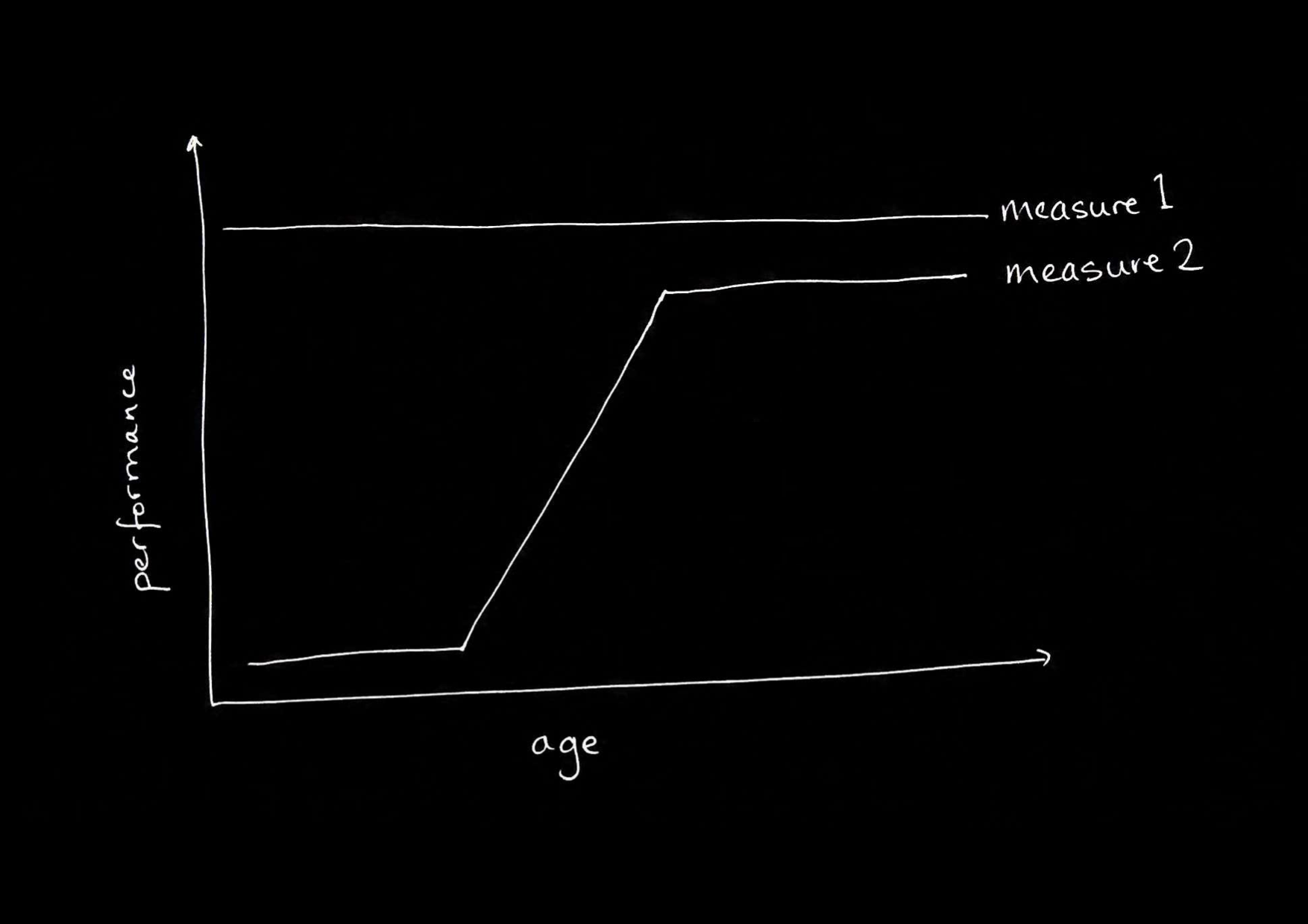
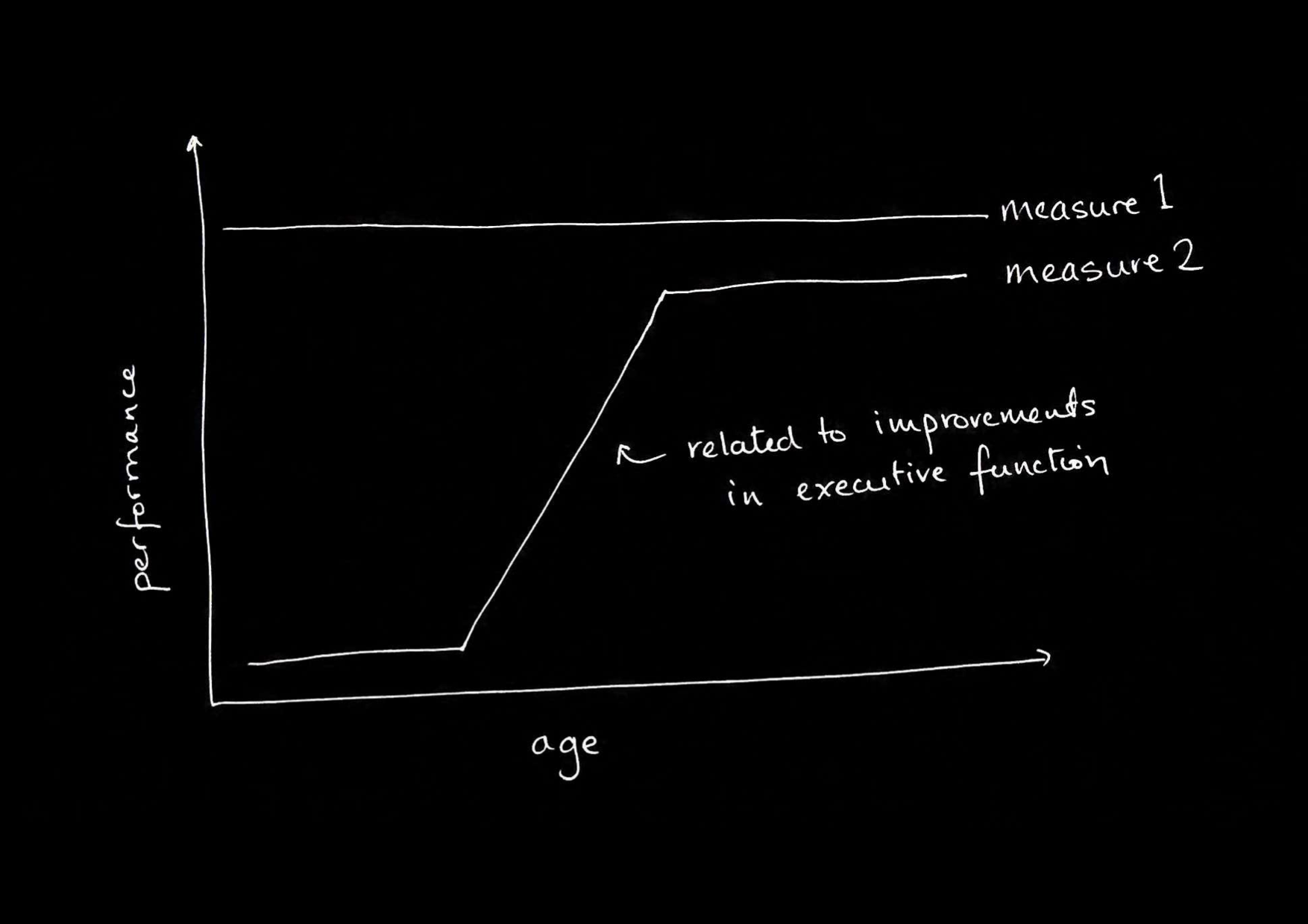
- different processing characteristics (e.g. automaticity).
- doubly inconsistent responses.
first conjecture:
There are two (or more) systems for tracking others’ beliefs.
(And some system for tracking beliefs in infants exists unchanged in adults.)

How do mindreaders’ belief-tracking systems model minds?
- compare -
How do physical thinkers model the physical?
1
theories of the physical/mental
2
efficiency-flexibility trade offs
‘an impetus heuristic could yield an approximately correct (and adequate) solution ... but would require less effort or fewer resources than would prediction based on a correct understanding of physical principles.’
Hubbard (2014, p. 640)
3
signature limits
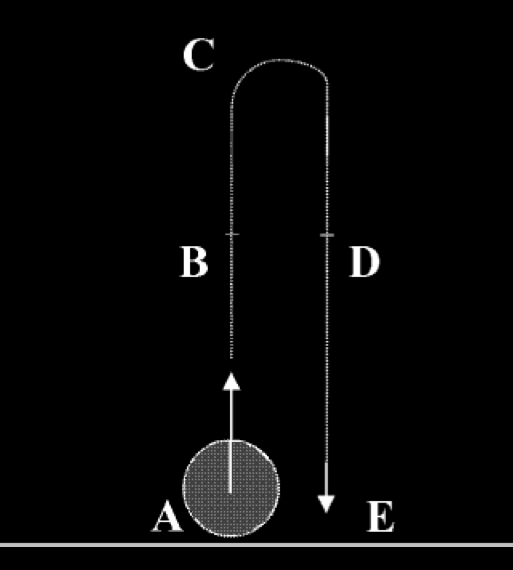
Kozhevnikov & Hegarty (2001, figure 1)
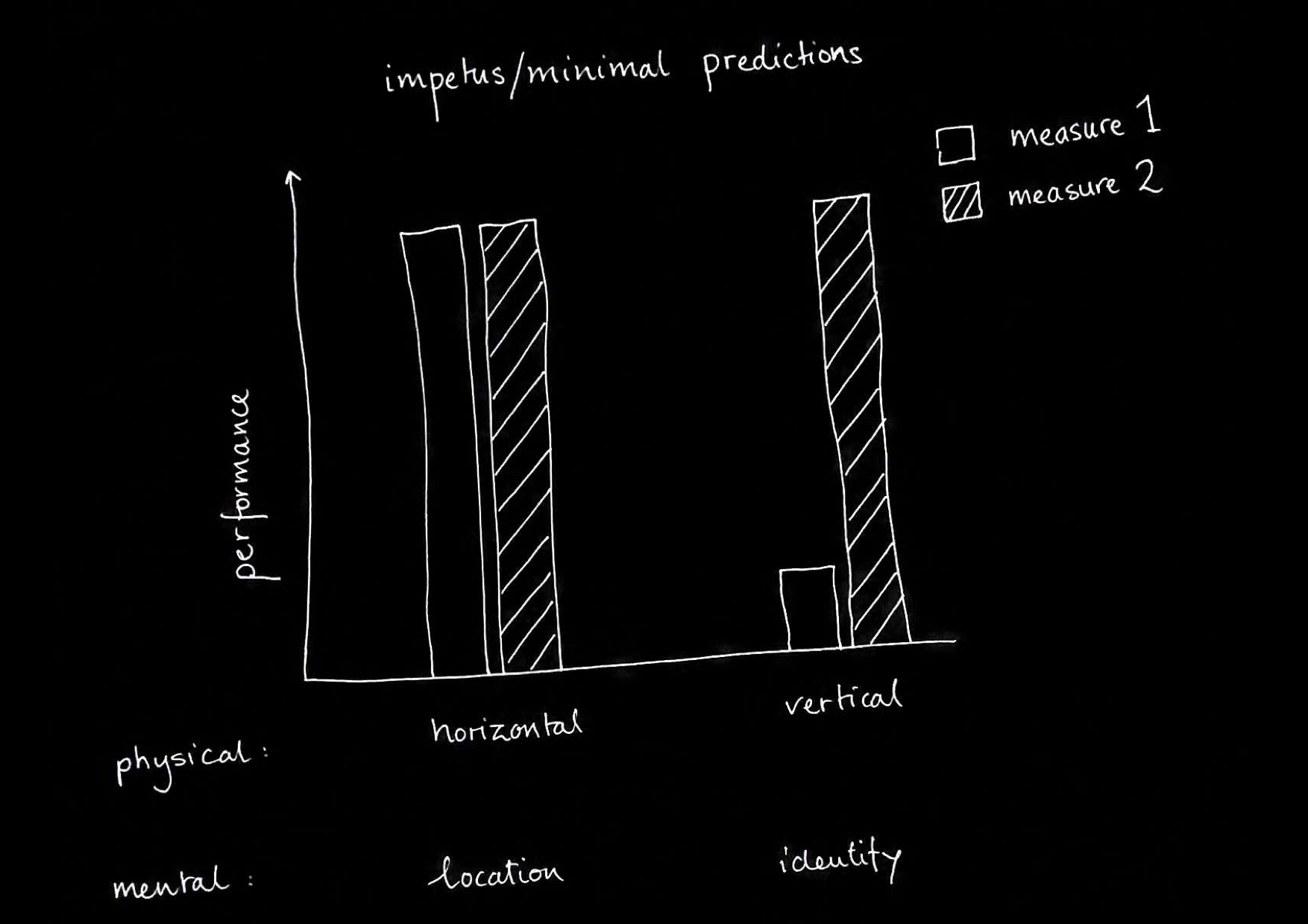
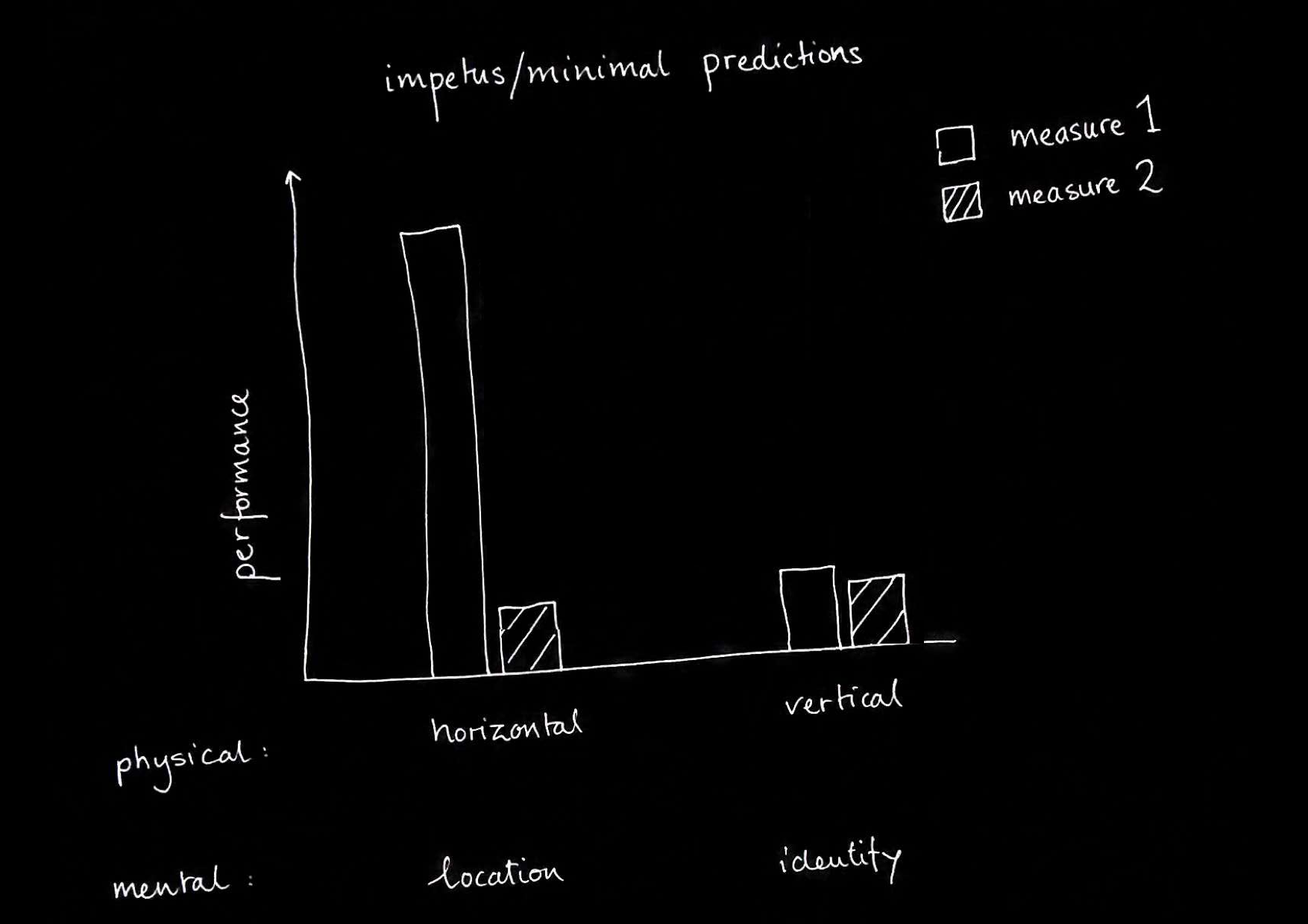
How do mindreaders’ belief-tracking systems model minds?
- compare -
How do physical thinkers model the physical?
theories of the mental:
full-blown vs minimal theory of mind


efficiency / flexibility?
signature limits
 |  |
signature limits
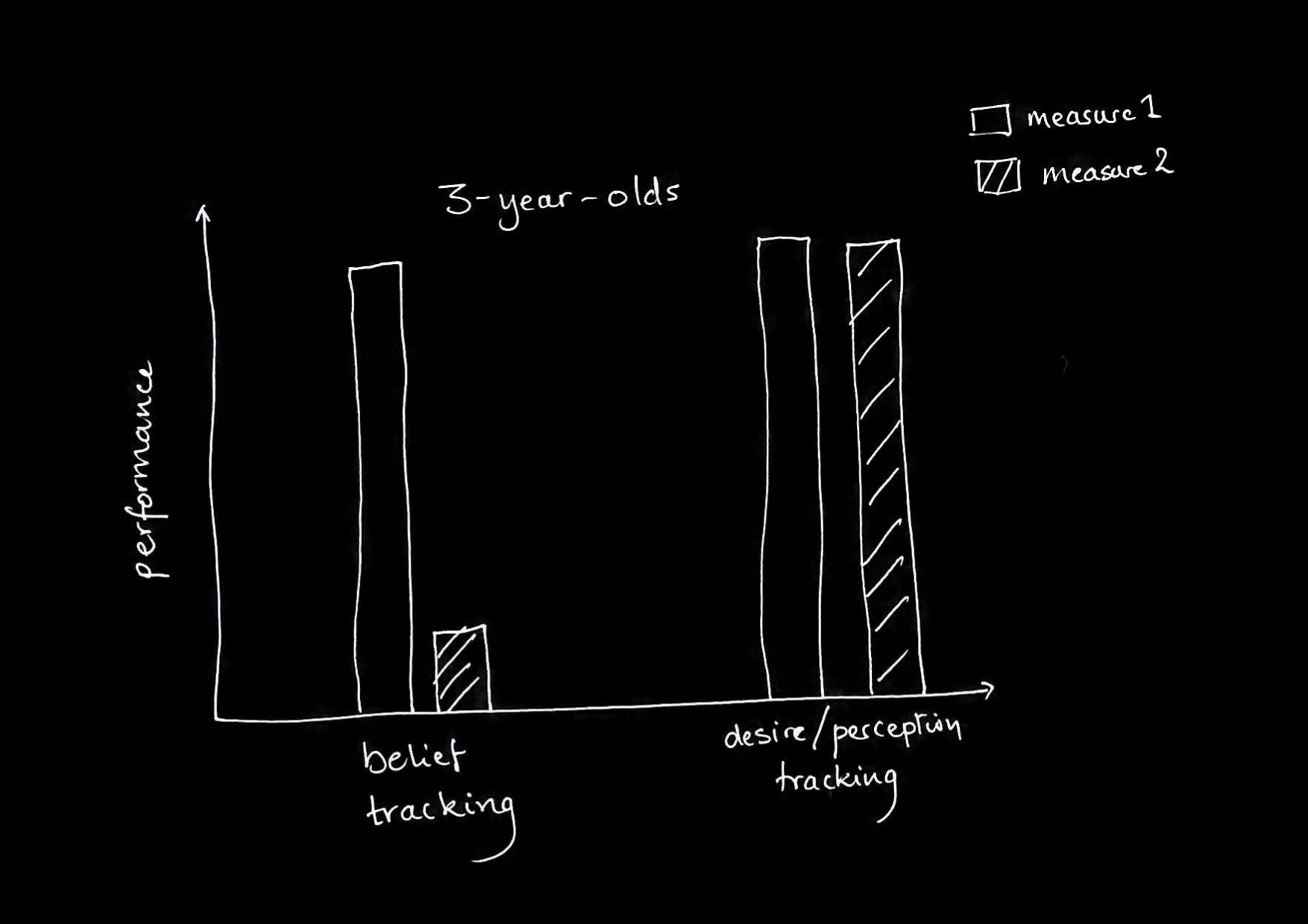
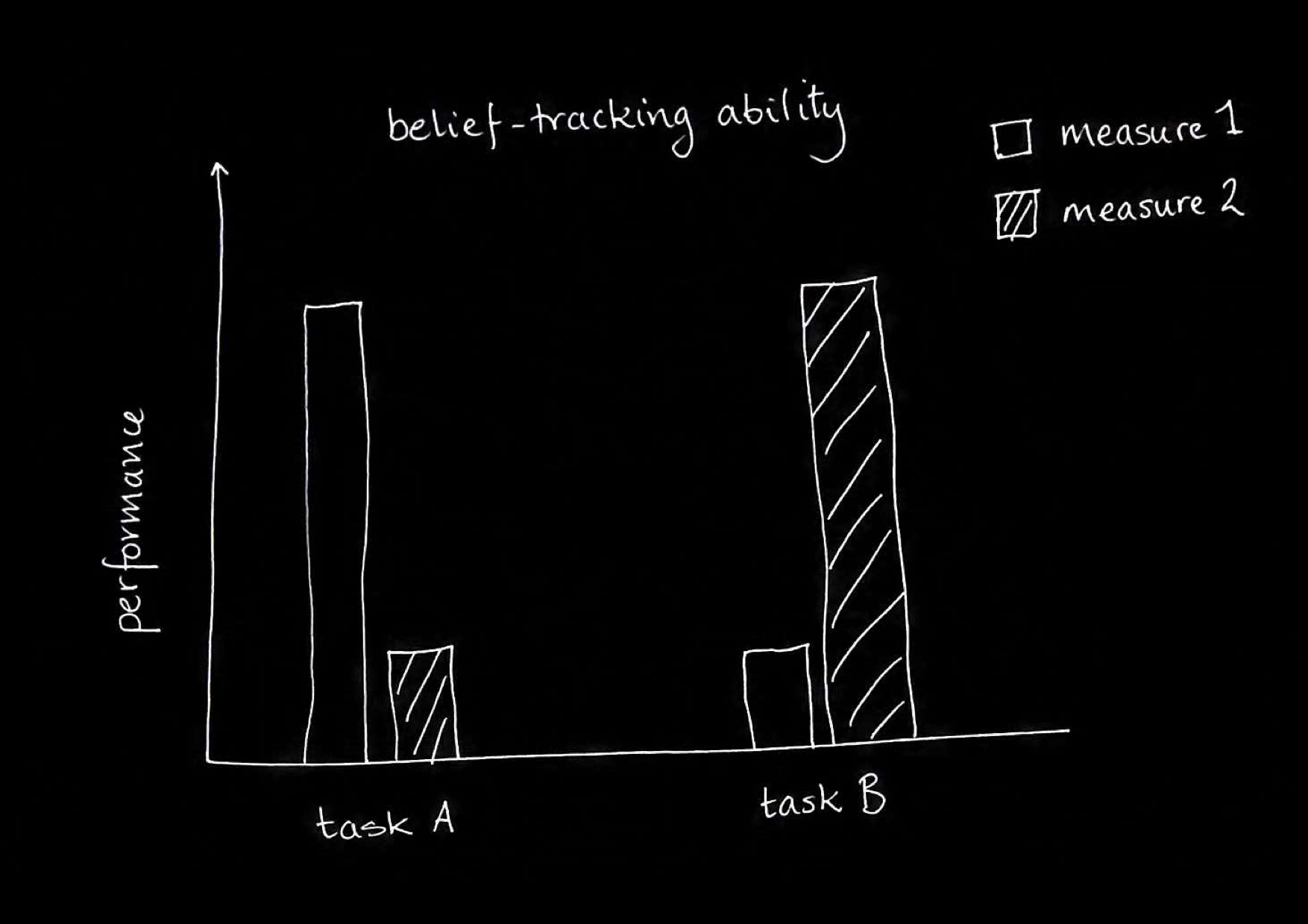
| full-blown theory of mind | minimal theory of mind | |
| false beliefs about location, colour, ... | Y | Y |
| false beliefs about identity, appearance ... | Y | N |
| level-1 perspective taking | Y | Y |
| level-2 perspective taking | Y | N |
second conjecture:
Some relatively efficient belief-tracking systems rely on minimal models of the mental.
predictions:
- In adults, some relatively efficient belief-tracking processes are subject to the signature limits.
- 0- and 1-year-olds’ belief-tracking is subject to the signature limits.

1. Systems
Conjecture: There are ≥ two belief-tracking systems
Predictions: different processing characteristics; doubly inconsistent responses.
2. Models
Conjecture: Some efficient* belief-tracking systems rely on minimal models.
Predictions: Infants’ & adults’ efficient belief-tracking are subject to signature limits.
(Background on models)
There are ≥ two models of the mental, full-blown and minimal.
Mindreading is the use of any model of the mental.
Different models allow different flexibility-efficiency trade offs.
We can distinguish models by signature limits.